With early hepatocellular cancer (HCC), you may not have any symptoms. More advanced HCC may have symptoms. They may be quite vague, especially if you already have symptoms from other liver disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis. You may just find you
- feel sick
- have no appetite, or feel full after eating very little
- lose weight without trying.
Other symptoms of HCC are listed below. Remember that many of them are common to other liver diseases. If you have hepatitis or cirrhosis, tell your doctor if you have any new symptoms or your symptoms are getting worse.
With HCC, you may have
- tummy (abdominal) pain – this happens in between 50 and 95 out of 100 people (50-95%)
- abdominal swelling (ascites)
- feeling generally unwell and lacking in energy (malaise)
- pain in your right shoulder – because the enlarged liver is irritating nerves that supply the shoulder
- jaundice – yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes
Ascites
Swelling may be caused by an enlarged liver or by fluid collecting in the tummy (abdomen). The liver is responsible for making proteins that keep fluid in the bloodstream. Without these, fluid tends to seep out and can pool around the abdominal organs.
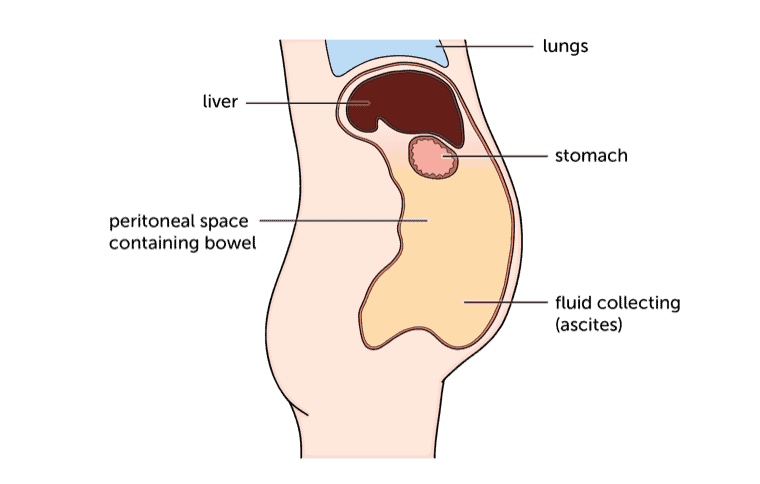
Doctors call this ascites (say: a-site-eez). You may also notice other swelling, such as puffy ankles.
Jaundice
Jaundice (say: jawn-diss) is caused by the cancer blocking one or more of the bile ducts. Bile then gets backed up in the liver, so you can’t get rid of bilirubin. This waste product from recycling red blood cells is normally processed by the liver. The bilirubin collects in the bloodstream and other body tissues, causing yellowing.
Other symptoms related to jaundice are:
- itching, caused by a build up of bile salts in the skin
- very dark wee from bilirubin in the urine
- pale, putty-coloured poo (bowel movements) because bile salts are not passing through and colouring the poo brown
Early on, you may have few other symptoms from jaundice. Later, it can cause flu-like symptoms, including fever, aching muscles and feeling weak and tired. You may also feel sick.
Less common symptoms
Around 1 in 5 people (20%) have odd symptoms caused by the liver tumours making hormones. Doctors call this paraneoplastic syndrome. One in 10 people (10%) have this when they first go to the doctor. The commonest are:
- high blood calcium, causing sickness, weakness and constipation. If not treated, patients become confused and increasingly drowsy
- low blood sugar causing tiredness, weakness and fainting
Sadly, in up to 4 out of 10 people (40%) the cancer has already spread before it’s diagnosed. If it has spread to the bones, you may have bone pain or sudden bone fractures for little or no reason. If it spreads to the lungs, it can cause cough and shortness of breath.
Mental changes
This isn’t really a symptom of HCC, but rather a complication of advanced liver disease. Doctors call it hepatic encephalopathy (say: en-keff-al-op-ath-ee). Toxins build up in the blood because the liver is not working well enough to remove them. They can cause mental changes, such as confusion, forgetfulness and poor concentration. If not treated people can become drowsy and confused.
Do talk to your doctor if you are concerned. They will be able to tell from your blood tests whether this is happening. But remember that many of us are forgetful at times, particularly when we’re stressed. And difficulty concentrating is common in people who’ve just had a cancer diagnosis.
Content last reviewed: October 2022
Next review date: October 2025
